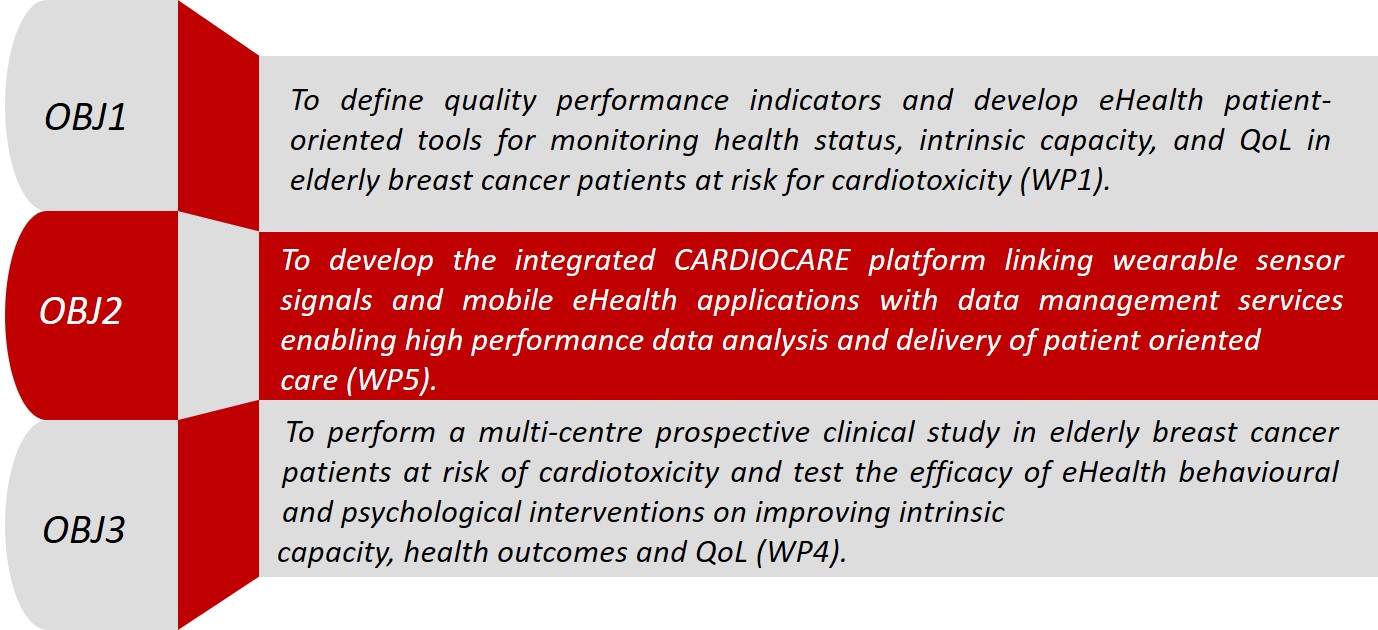
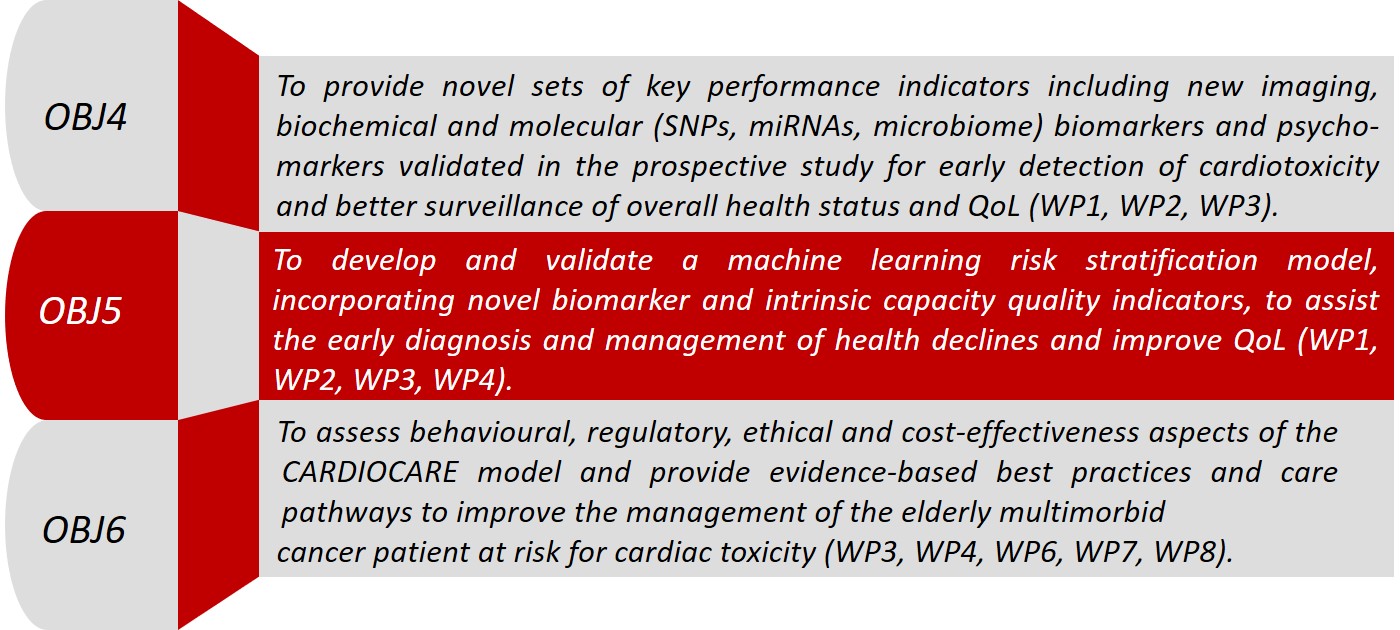
More than 50% of the newly diagnosed breast cancer patients are elderly and particularly susceptible to cardiotoxicity of cancer treatment due to age-related factors and the prevalence of multiple co-morbidities. The cumulative effect of risk factors in the elderly patient resembles a “snowball effect”, where baseline age and cancer-related changes are exacerbated by direct therapy-induced cardiotoxicity, resulting in a multi-morbid state and mortality. Frailty and high risk of cardiotoxicity in this group may lead to inappropriate interventions and undertreatment, resulting in poorer outcomes, deterioration of QoL and increased healthcare costs. Considering, that older cancer patients are underrepresented in trials, new interdisciplinary and patient-oriented studies able to provide clinical guidelines and best practices for delivering quality care are needed.
CARDIOCARE will contribute to scaling up better management for the multimorbid elderly breast cancer patients. Innovative eHealth applications, coupled with sensors and wearables, will permit a consistent evaluation of the intrinsic capacity and by combining clinical and biological features, will provide a holistic approach to the management of cancer and its co-morbidities in the elderly population. This will allow the development of quality indicators for effective care pathways and allow a more informed approach to breast cancer patients with multimorbidity, training and education of caregivers and stakeholders to boost effectively elderly breast cancer patients along disease trajectory and cardiotoxicity. eHealth applications will increase the involvement and participation of the patients in their care process and self-management improving adherence to their individualized care plan, and a better psychological adaptation to their disease. Overall, the implementation of a comprehensive model for effective risk stratification will positively impact QoL, adverse events, hospitalizations, and healthcare.